Demystifying Support Vector Machines: A Comprehensive Guide
**Introduction**
In the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence and machine learning, Support Vector Machines (SVMs) emerge as a game-changer. From classification to regression and even outlier detection, SVMs have marked their territory across diverse domains. Join us in this comprehensive guide to delve into the world of Support Vector Machines, unraveling their core concepts, mechanics, and real-world applications.
**Table of Contents**
1. **Cracking the Code of Support Vector Machines**
– Demystifying SVMs
– Top Advantages Unveiled
2. **The Math Behind the Magic**
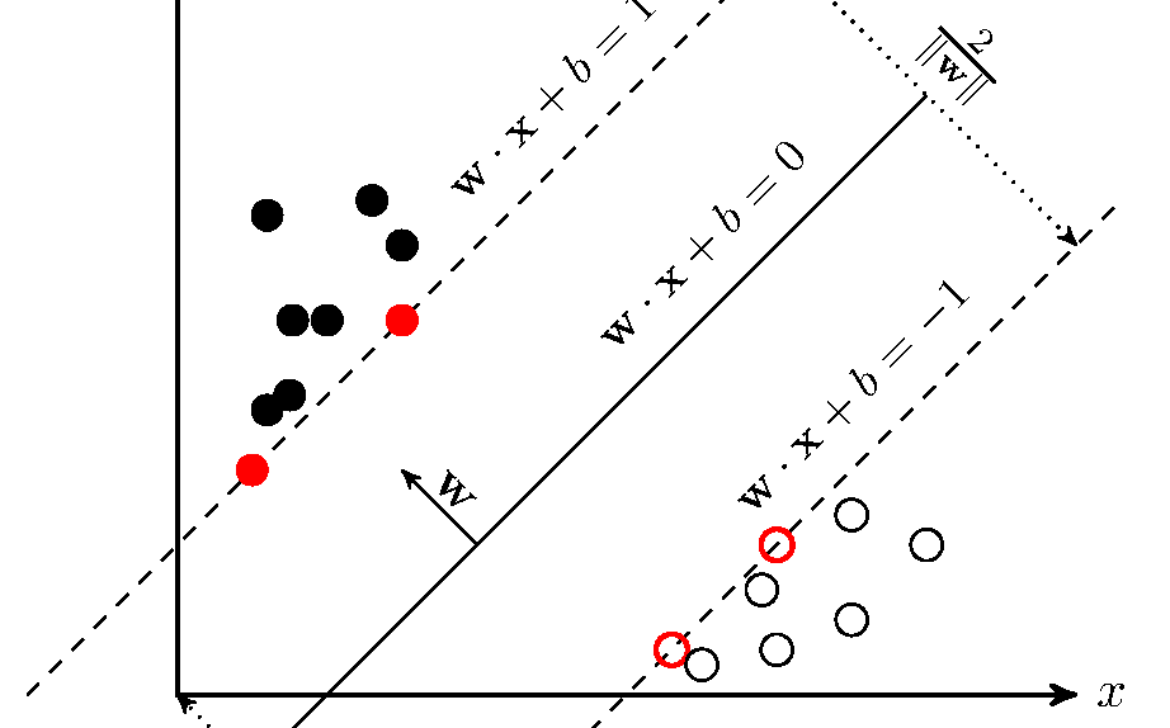
– Grasping Hyperplanes and Margin
– Unveiling the Maximum Margin Classifier
– Navigating the Soft Margin Territory
3. **Kernel Trick: Amplifying Possibilities**
– Tackling Linearly Inseparable Data
– Mastering the Art of Kernels
– Exploring Must-Know Kernels (Linear, Polynomial, RBF)
4. **Inner Workings of Support Vector Machines**
– Decoding Margin and Support Vectors
– Untangling the Quest for the Optimal Hyperplane
– Flexing Muscle with Kernel-driven Nonlinear Solutions
5. **Training and Optimizing SVMs**
– The Convex Optimization Puzzle
– Dancing with Lagrange Multipliers and the Dual Problem
– Masterstroke: Cracking the Dual Problem
6. **Putting SVMs into Action**
– Empowering with Leading Libraries (scikit-learn, LIBSVM)
– Navigating the Terrain: Data Prep and Feature Scaling
– Victory Lap: Training, Fine-tuning, and Smart Evaluation
7. **Extensions and Flavors**
– Stepping into Support Vector Regression (SVR)
– Conquering Multi-class Classification Challenges
– Spotlight: Anomaly Detection with One-Class SVM
8. **Savvy Strategies for SVM Mastery**
– The Kernel Conundrum: Choosing Right
– Slaying Giants: SVMs with Big Data
– Balancing Act: Triumphing over Imbalanced Data
9. **Real-world Triumphs**
– Picture Perfect: Image Classification Wins
– Text Titan: SVMs in Text and Document Classification
– Lifesaver: SVMs in Bioinformatics and Medical Diagnostics
10. **SVMs vs. the World**
– Cage Match: SVM vs. Logistic Regression
– Clash of Titans: SVM vs. Decision Trees
– Battle Royale: SVM vs. Neural Networks
11. **Nitty-gritty Challenges**
– Tackling Complexity Head-on
– Secret Sauce: Navigating Hyperparameters
– Taming the Wild: Gaining Insights with Interpretable SVMs
12. **Beyond Horizons: Future of SVMs**
– Kernel Wonders on the Horizon
– Unleashing SVM Potential in Deep Learning
– Fusion Power: Hybrid Models and Unstoppable Ensembles
**Conclusion**
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are the stars of the machine learning cosmos, offering both theoretical elegance and real-world prowess. This comprehensive SEO-optimized guide has unveiled the essence of SVMs, their mathematical essence, practical deployment strategies, and feats in diverse applications. You’re now primed to embark on your SVM journey, armed with the insights to tackle classifications, regressions, and intricate data patterns. Seize the opportunity to harness the might of Support Vector Machines, and open new doors in the world of AI and beyond. Your SVM-powered breakthrough awaits!