The gig economy has been a rapidly growing sector in the global labor market, with increasing numbers of people relying on temporary and flexible work arrangements. This has both positive and negative impacts on workers and society as a whole. In this blog, we will explore the various ways the gig economy has affected workers and society, and discuss the potential future implications of this evolving labor landscape.
The Benefits of the Gig Economy for Workers
The gig economy offers numerous benefits for workers, particularly for those who value flexibility and autonomy in their work. Some of the advantages include:
Flexibility: Workers in the gig economy can choose when and where they work, allowing them to better balance their professional and personal lives. This is especially appealing to individuals who have family or other personal commitments that may not align with traditional 9-to-5 work schedules.
Income diversification: The gig economy allows workers to engage in multiple streams of income, which can help them reduce financial risk and stabilize their overall income.
Skill development: The gig economy often requires workers to develop new skills and adapt to different types of work, which can help them become more versatile and marketable in the job market.
Entrepreneurial opportunities: For some, the gig economy provides a platform to launch their own businesses or side hustles, enabling them to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams.
The Challenges of the Gig Economy for Workers
Despite the benefits, the gig economy also presents several challenges for workers, including:
Lack of job stability and security: Gig economy workers typically do not have the same job security as traditional employees, as their contracts can be terminated at any time and without notice.
Limited access to benefits: Gig economy workers often lack access to traditional employee benefits such as healthcare, retirement savings, and paid time off. This can create financial stress for many workers.
Difficulty in advancing their careers: The gig economy can make it harder for workers to advance their careers, as they may not have access to the same training and development opportunities as traditional employees.
Exploitation and unfair treatment: Some gig economy platforms have been criticized for taking advantage of workers by paying them low wages and not providing appropriate protections.
The Impact of the Gig Economy on Society
The gig economy has also had a significant impact on society as a whole. Some of these effects include:
Economic growth: The gig economy has contributed to economic growth by creating new job opportunities and fostering innovation.
Changing workforce demographics: The gig economy has led to an increase in self-employment and the growth of the “gig” workforce, which includes both full-time and part-time workers.
Disruption of traditional industries: The gig economy has disrupted traditional industries such as transportation (e.g., Uber and Lyft) and hospitality (e.g., Airbnb), forcing these industries to adapt to new business models.
Income inequality: The gig economy has been criticized for contributing to income inequality, as many gig economy workers earn low wages and lack access to traditional benefits.
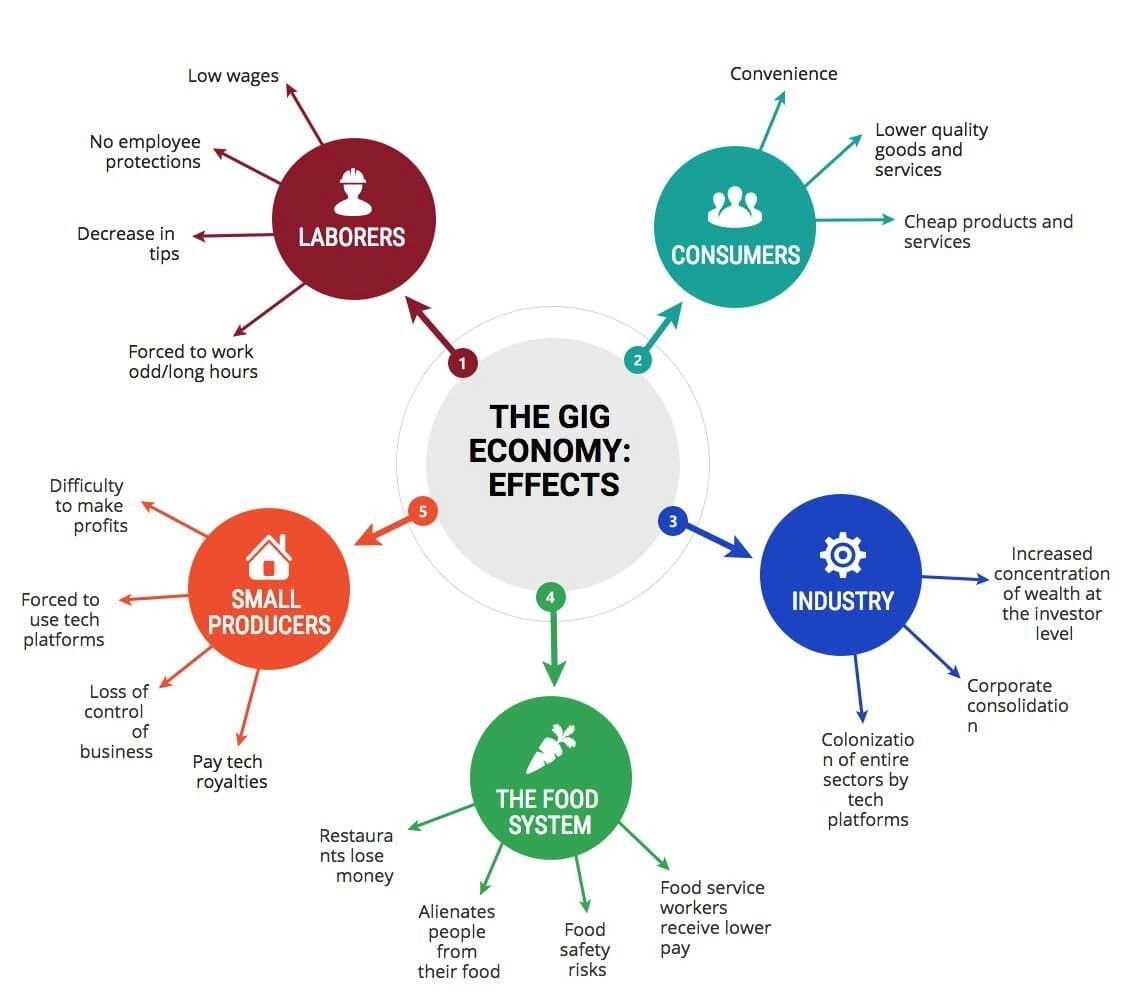
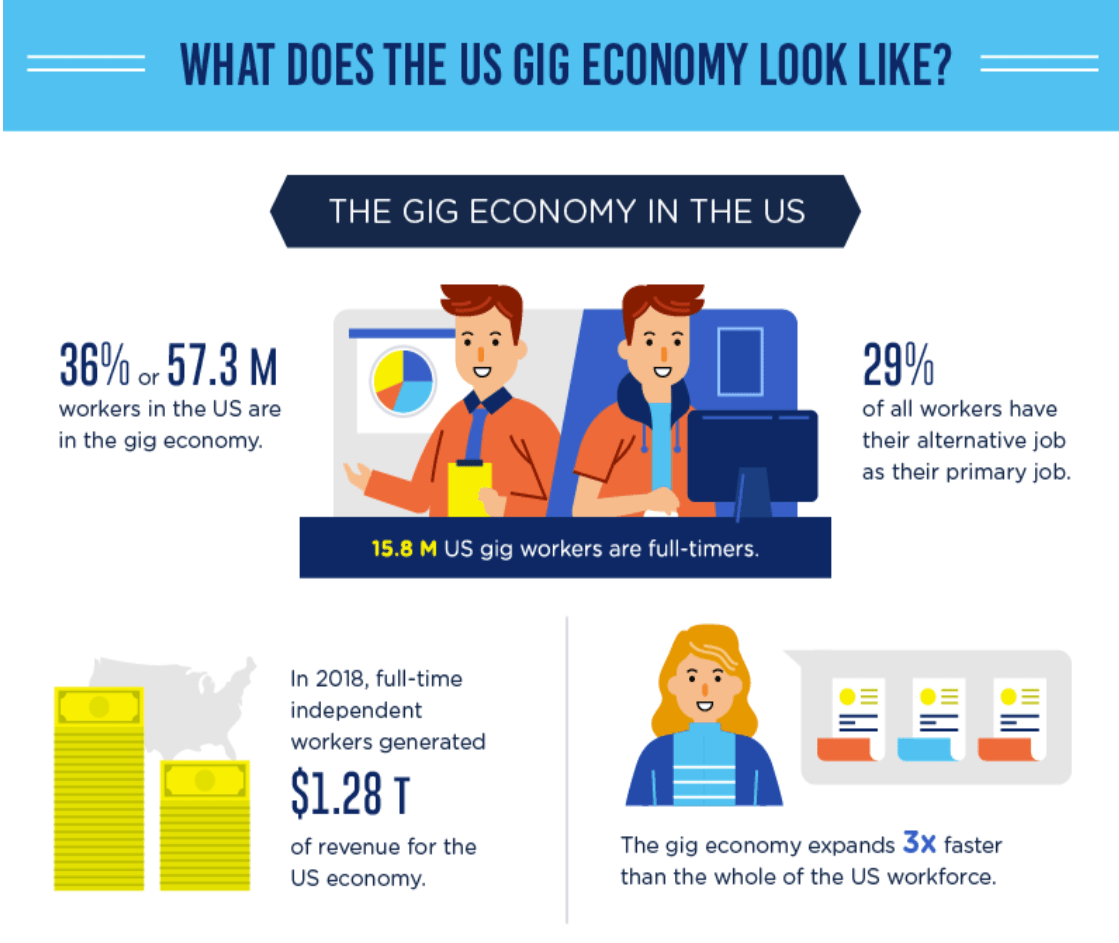
Conclusion
The gig economy has both positive and negative impacts on workers and society. While it offers increased flexibility and entrepreneurial opportunities for some, it also presents challenges such as job insecurity and limited access to benefits. As the gig economy continues to grow, it is essential for governments, businesses, and workers to work together to address these challenges and ensure a fair and sustainable labor market for all.




