Safeguarding the Digital Realm: Unveiling the Importance of Cybersecurity
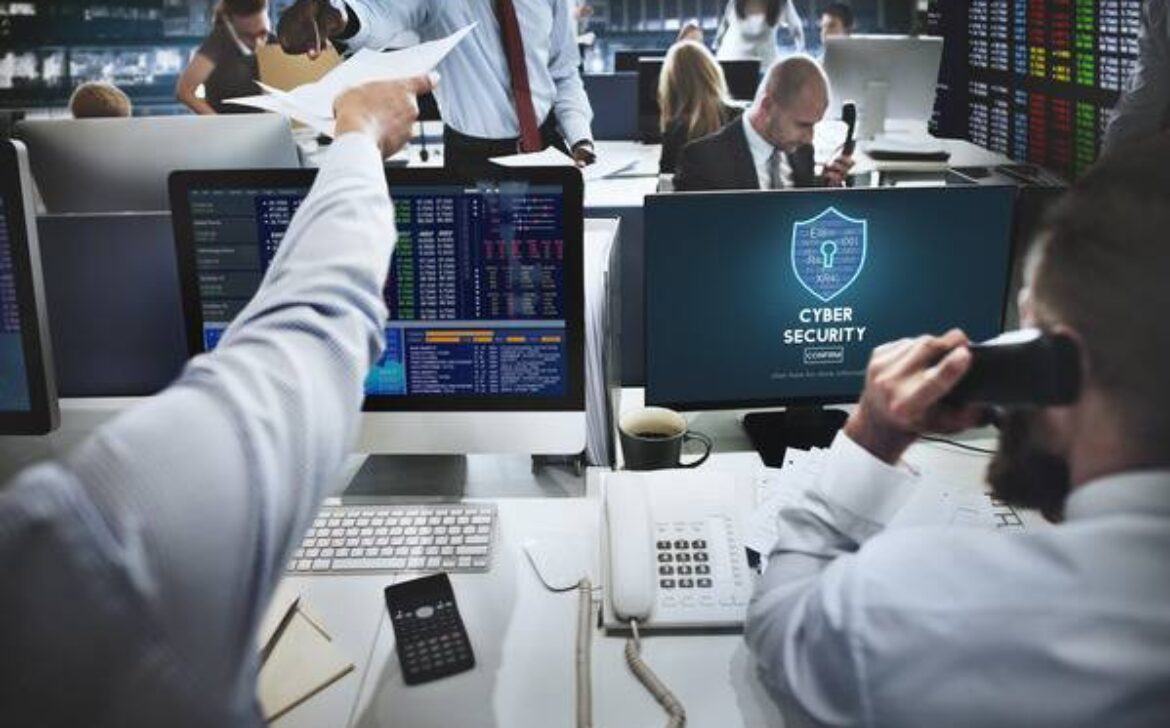
In the present era of a globally connected society, where technology intertwines with every facet of our existence, safeguarding the integrity of our digital domain has emerged as an unparalleled imperative. Cybersecurity plays a vital role in protecting our personal information, sensitive data, and critical systems from malicious actors who seek to exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain. In this article, we will explore the significance of cybersecurity, common cyber threats, best practices to enhance online security, and the importance of cybersecurity in the business environment. In an era dominated by digital advancements, cybersecurity has emerged as a crucial defense mechanism against cyber threats. It encompasses the practices and measures implemented to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities. Cybersecurity refers to the collective efforts and techniques employed to safeguard computer systems, networks, software, and data from unauthorized access, damage, theft, or disruption. It involves the application of robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets. The importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, cyber threats have become more sophisticated and prevalent. A successful cyber attack can result in severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised personal and sensitive information. Effective cybersecurity measures are crucial in mitigating these risks and maintaining the trust of individuals and businesses in the digital realm. Cyber threats come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and potential impact. A selection of the prevailing cyber hazards encompasses: Phishing attacks involve the use of deceptive techniques to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or social security numbers. Frequently, these malicious assaults transpire via electronic communications, such as emails, messages, or counterfeit websites meticulously crafted to present an illusion of authenticity. Malware refers to malicious software designed to infiltrate systems and disrupt their normal operations. This includes viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. Malware can be spread through infected email attachments, downloads from untrusted sources, or compromised websites. Social engineering encompasses the art of skilfully manipulating individuals with the aim of obtaining unauthorized entry into systems or extracting confidential information. It relies on psychological manipulation and often exploits human vulnerabilities such as trust, fear, or ignorance. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a network or website with a flood of incoming traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks typically utilize a network of compromised computers, known as a botnet, to generate the excessive traffic.
The only truly secure system is one that is powered off, cast in a block of concrete, and sealed in a lead-lined room with armed guards.
– Gene Spafford To enhance cybersecurity and protect against these threats, it is essential to adopt best practices: Developing robust and distinctive passwords serves as the initial barrier to prevent unauthorized entry. Employ a blend of uppercase and lowercase letters, numerical digits, and special symbols, while refraining from utilizing easily predictable details like personal names or birthdates. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification beyond a password. This could be a unique code sent to a mobile device or a biometric factor like a fingerprint. Regularly updating software, including operating systems and applications, helps protect against known vulnerabilities. Software updates often include security patches that address newly discovered weaknesses. Frequent backups of important data are crucial to mitigate the impact of potential data breaches or system failures. Store backups in secure off-site locations or utilize cloud-based backup solutions. Mistakes made by individuals play a substantial role in cyber breaches. Training employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as identifying phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and recognizing social engineering tactics, can greatly reduce the risk of successful attacks. Firewalls act as barriers between internal networks and external sources, filtering out unauthorized access attempts. Antivirus software helps detect and remove malicious software from systems, providing an additional layer of protection. Implementing intrusion detection systems and monitoring tools allows for the early detection of cyber attacks. Swift incident response plans and effective mitigation strategies help minimize the impact of potential breaches. Encryption ensures that sensitive data remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals. By converting data into a format that can only be decrypted with a specific key, encryption protects information in transit and at rest. Safeguarding personal information, such as social security numbers, credit card details, and addresses, is crucial to prevent identity theft and financial fraud. Adhere to privacy regulations and limit the sharing of personal information online. Businesses must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard their digital assets and maintain operational continuity. Implementing robust security measures, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and enforcing strict access controls are critical steps in protecting sensitive business data. In an increasingly digital landscape, cybersecurity plays a pivotal role in ensuring the protection and integrity of our digital realm. By understanding the significance of cybersecurity, recognizing common threats, and adopting best practices, individuals and organizations can enhance their online security posture. Protecting our digital assets is not only essential for personal privacy but also critical for the stability and trustworthiness of the interconnected digital ecosystem.Introduction
What is Cybersecurity?
The Significance of Cybersecurity



Common Cyber Threats
1. Phishing Attacks
2. Malware Infections
3. Social Engineering
4. DDoS Attacks
Cybersecurity Best Practices
Importance of Strong Passwords
Utilizing Two-Factor Authentication
Keeping Software Up-to-Date
Regular Data Backups
Educating Employees on Cybersecurity
Implementing Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Detecting and Responding to Cyber Attacks
Importance of Encryption
Protecting Personal Information
Cybersecurity in the Business Environment
Conclusion