Social Engineering: Art of Manipulating People for Cyber Attacks
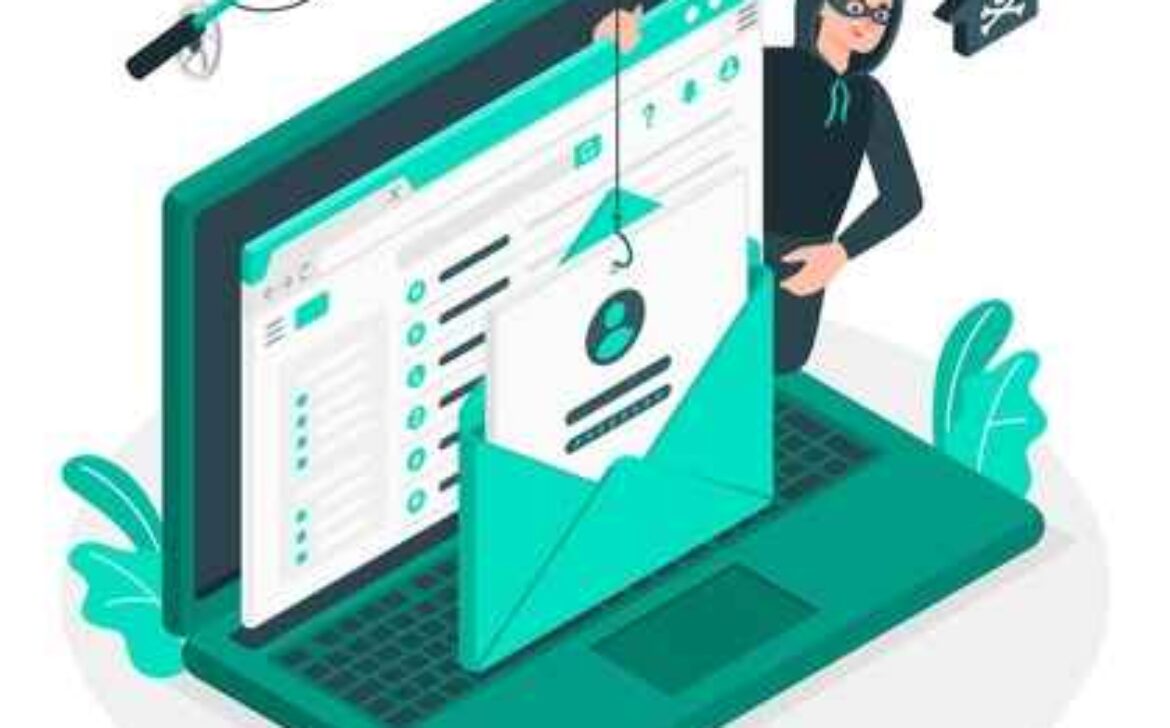
Social engineering is the use of psychological tactics to manipulate people into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that could be detrimental to their security. Social engineering attacks can come in many forms, including phishing emails, pretexting phone calls, baiting scams, and more. The ultimate goal of social engineering is to bypass technical security measures by exploiting human weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals use social engineering to trick victims into revealing passwords, downloading malicious software, or giving access to sensitive information. Social engineering attacks can happen to anyone, regardless of how tech-savvy they are. In fact, social engineering attacks have become increasingly sophisticated over the years, making them harder to detect and more convincing. One of the most common social engineering attacks is phishing, where attackers use fraudulent emails or websites to trick users into providing sensitive information. These emails often appear to be from a trusted source, such as a bank, social media platform, or government agency.
The weakest link in cybersecurity is the human element, and social engineering preys on our innate desire to trust and help others Another type of social engineering attack is pretexting, where an attacker pretends to be someone else to gain access to sensitive information. For example, an attacker might call an employee pretending to be an IT support technician and ask for their login credentials. In conclusion, social engineering attacks are a growing threat in today’s digital landscape, and businesses and individuals must take proactive measures to protect themselves. By staying informed and implementing best practices for cybersecurity, we can minimize the risks of falling victim to these types of attacksSocial Engineering



Some tips to protect against social engineering attacks