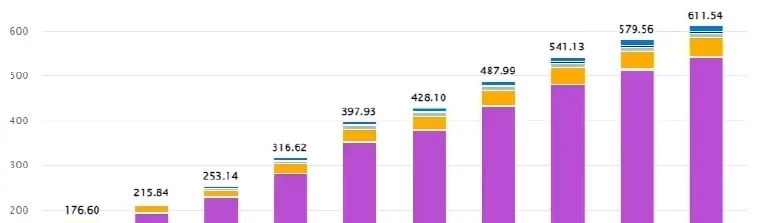
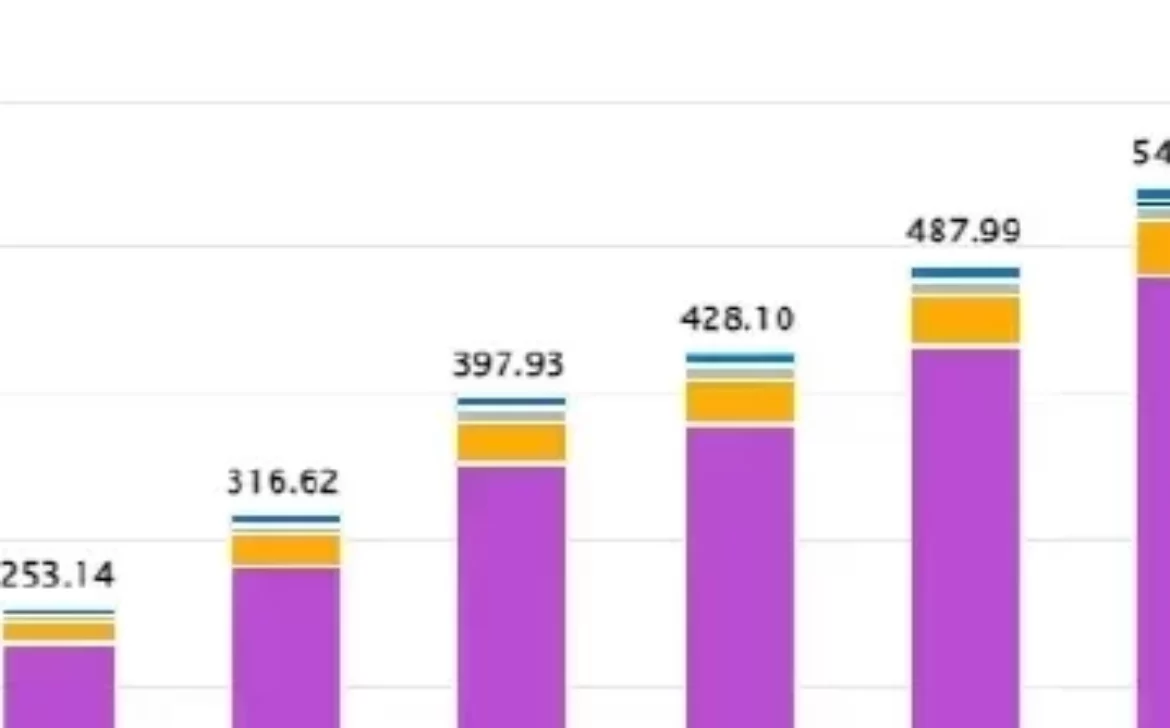
“The Evolution of Mobile Apps: Trends and Innovations”
The evolution of mobile apps has been remarkable, with constant advancements and innovations shaping the way we interact with our smartphones and mobile devices. Here are some prominent trends and innovations that have emerged in the mobile app landscape: Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies have gained significant traction in mobile app development. AR apps overlay digital information and virtual objects onto the real world, enhancing user experiences in areas such as gaming, retail, education, and navigation. VR apps, on the other hand, create immersive virtual environments, opening up possibilities for entertainment, training, and simulation experiences. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI has transformed mobile apps by enabling intelligent features and personalized experiences. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer support and provide instant responses. AI algorithms analyze user behavior, preferences, and data to offer tailored recommendations, content, and notifications. Voice assistants, such as Siri and Google Assistant, have become common features in mobile apps, allowing users to interact with apps using natural language commands. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Mobile apps have become integral components of IoT ecosystems. They connect and control various smart devices, allowing users to remotely monitor and manage their homes, cars, wearables, and other IoT-enabled devices. Mobile apps provide real-time data and control capabilities, enabling users to interact with and optimize their connected environments. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs are web applications that offer app-like experiences on mobile devices. They leverage modern web technologies to provide offline capabilities, push notifications, and device hardware access. PWAs eliminate the need for traditional app installations, making them accessible through web browsers, reducing data consumption, and enhancing user convenience. Mobile Wallets and Contactless Payments: Mobile apps have revolutionized payment systems, with mobile wallets becoming increasingly popular. Apps like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay enable users to make secure, contactless payments using their smartphones or wearables. Integration with Near Field Communication (NFC) technology allows users to tap their devices on payment terminals to complete transactions quickly and securely. Enhanced Security and Privacy Measures: With growing concerns around data privacy and security, mobile apps have adopted stricter security measures. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, have become common for unlocking devices and securing sensitive app information. App developers are also implementing encryption, secure protocols, and data anonymization techniques to protect user data. Instant Apps: Instant apps allow users to access specific app functionalities without installing the complete app. Users can try out the app before deciding to install it, saving storage space and data usage. Instant apps provide a frictionless experience and have become a popular approach for app discovery and user acquisition. Cross-Platform Development: Developers are increasingly adopting cross-platform development frameworks, such as React Native and Flutter, to build apps that work seamlessly across multiple platforms, including iOS and Android. This approach reduces development time and costs while maintaining a consistent user experience. Mobile Gaming: The mobile gaming industry has witnessed significant growth, driven by advanced graphics, immersive experiences, and multiplayer capabilities. Games like Pokémon Go and Fortnite have demonstrated the potential of mobile gaming to create social interactions and engage millions of users worldwide. App Analytics and Personalization: Mobile app developers are leveraging analytics tools to gain insights into user behavior, app usage patterns, and performance metrics. These insights help optimize user experiences, identify areas for improvement, and personalize app content, notifications, and recommendations based on user preferences. The evolution of mobile apps continues to shape our digital experiences, opening up new possibilities for communication, productivity, entertainment, and commerce. As technology advances, we can expect further innovations that enhance user experiences and redefine how we interact with mobile devices.