Navigating the Cybersecurity Landscape

INFORMATION:
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, damage, or theft. It encompasses a range of technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard digital information and assets against various threats, including malware, phishing, ransomware, and other forms of cybercrime. The goal of cybersecurity is to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems, ensuring they remain secure and operational in the face of potential threats and vulnerabilities.
IMPORTANCE:
Protection of Sensitive Data:
In today’s digital world, businesses and individuals store vast amounts of sensitive information online, including personal data, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Effective cybersecurity measures help safeguard this data from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse.
Preservation of Privacy:
Cybersecurity ensures that individuals’ and organizations’ privacy rights are respected by preventing unauthorized parties from accessing or monitoring their online activities, communications, and personal information.
Prevention of Financial Loss:
Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses for businesses and individuals through theft, fraud, extortion, or disruption of operations. Strong cybersecurity defenses help mitigate these risks by reducing the likelihood and impact of successful cyberattacks.
Protection of Infrastructure:
Critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, transportation, healthcare, and finance rely heavily on interconnected computer systems and networks. Cybersecurity safeguards these systems from attacks that could disrupt essential services, endanger public safety, or cause economic damage.

Here’s how cybersecurity helps:
Fraud Detection Systems:
Advanced fraud detection systems analyze patterns of user behavior and transaction data to identify suspicious activities, such as unusual spending patterns or login attempts from unfamiliar locations. These systems can automatically flag and investigate potentially fraudulent transactions, protecting users from financial loss.
Educational Awareness:
Cybersecurity awareness programs educate users about common frauds and scams, empowering them to recognize warning signs and take appropriate actions to protect themselves. Training programs cover topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and safe online practices.
Secure Online Transactions:
Secure sockets layer (SSL) encryption and transport layer security (TLS) protocols ensure that online transactions, such as e-commerce purchases and online banking, are conducted securely, protecting users’ financial information from interception and unauthorized access.
CONCLUSION:
Cybersecurity is not just a necessity but a critical aspect of our digital lives, protecting us from a myriad of threats such as frauds and scams. As our reliance on technology continues to grow, so too does the importance of safeguarding our digital assets and personal information.
The Impact of DevOps in Today’s Digital Landscape

Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and fiercely competitive digital landscape, the need for speed, agility, and innovation has never been more critical. As organizations strive to deliver products and services at an unprecedented pace while maintaining high levels of quality and reliability, traditional software development and operations approaches often fall short. This is where DevOps comes into play, revolutionizing the way software is built, deployed, and managed. Let’s delve into the impact of DevOps in today’s world, why it’s needed, its benefits, and draw a conclusion on its significance.
Why DevOps is Needed

Alignment of Development and Operations:
DevOps bridges the gap between development and operations teams, fostering collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility throughout the software development lifecycle. This alignment ensures that development and operations work seamlessly together, leading to faster delivery cycles and improved efficiency.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
DevOps practices enable organizations to implement CI/CD pipelines, automating the process of building, testing, and deploying software. By automating repetitive tasks and reducing manual intervention, CI/CD pipelines accelerate the delivery of new features and updates, allowing organizations to respond quickly to market demands.
Scalability and Flexibility:
With DevOps, organizations can leverage cloud infrastructure and containerization technologies to achieve greater scalability and flexibility. By dynamically provisioning resources and deploying applications in lightweight containers, DevOps enables organizations to scale their infrastructure and applications based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.

Benefits of DevOps
Faster Time to Market:
DevOps practices enable organizations to deliver software updates and new features to market quickly and efficiently, reducing time to market and gaining a competitive edge.
Improved Quality and Reliability:
By implementing automated testing, continuous monitoring, and proactive error detection, DevOps helps organizations improve the quality and reliability of their software, minimizing defects and downtime.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication:
DevOps promotes a culture of collaboration, transparency, and accountability across development, operations, and other stakeholders, fostering innovation and driving organizational success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DevOps has emerged as a transformative approach to software development and operations, revolutionizing the way organizations build, deploy, and manage software. By aligning development and operations, implementing CI/CD pipelines, and leveraging automation and cloud technologies, DevOps enables organizations to accelerate innovation, improve efficiency, and deliver value to customers at scale. In today’s digital landscape, where speed, agility, and innovation are paramount, DevOps is not just a methodology but a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to thrive in a rapidly evolving market.
Christmas Cheer

Introduction:
Christians consider Jesus Christ to be the Son of God, and Christmas is a time to remember his birth. The Mass of Christ is where the word “Christmas” originates (or Jesus). Christians commemorate the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ during a Mass ceremony, sometimes known as Communion or Eucharist.
Content:-
Gathering of Loved Ones: Christmas is a time for families to come together, often traveling from near and far to celebrate the holiday with one another.
Decorating the Home: One of the first activities families often do together is decorate their home for Christmas. This may include putting up a Christmas tree, hanging lights and ornaments, setting up nativity scenes.
Exchanging Gifts: In Christmas, friends and family members exchange presents with one another, often placing them under the Christmas tree to be opened on Christmas morning.
Attending Religious Services: For families who observe the religious aspect of Christmas, attending church services is a significant part of the celebration.
Creating Memories: Beyond the specific activities and traditions, Christmas is a time for families and friends to create lasting memories together.

Conclusion:
Christmas is a time of joy, celebration, and togetherness, marked by traditions, gifts, and festive decorations. It brings people closer, fosters goodwill, and encapsulates the spirit of giving.
The Impact of the Gig Economy on Workers and Society
The gig economy has been a rapidly growing sector in the global labor market, with increasing numbers of people relying on temporary and flexible work arrangements. This has both positive and negative impacts on workers and society as a whole. In this blog, we will explore the various ways the gig economy has affected workers and society, and discuss the potential future implications of this evolving labor landscape. The gig economy offers numerous benefits for workers, particularly for those who value flexibility and autonomy in their work. Some of the advantages include: Flexibility: Workers in the gig economy can choose when and where they work, allowing them to better balance their professional and personal lives. This is especially appealing to individuals who have family or other personal commitments that may not align with traditional 9-to-5 work schedules. Income diversification: The gig economy allows workers to engage in multiple streams of income, which can help them reduce financial risk and stabilize their overall income. Skill development: The gig economy often requires workers to develop new skills and adapt to different types of work, which can help them become more versatile and marketable in the job market. Entrepreneurial opportunities: For some, the gig economy provides a platform to launch their own businesses or side hustles, enabling them to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams. Despite the benefits, the gig economy also presents several challenges for workers, including: Lack of job stability and security: Gig economy workers typically do not have the same job security as traditional employees, as their contracts can be terminated at any time and without notice. Limited access to benefits: Gig economy workers often lack access to traditional employee benefits such as healthcare, retirement savings, and paid time off. This can create financial stress for many workers. Difficulty in advancing their careers: The gig economy can make it harder for workers to advance their careers, as they may not have access to the same training and development opportunities as traditional employees. Exploitation and unfair treatment: Some gig economy platforms have been criticized for taking advantage of workers by paying them low wages and not providing appropriate protections. The gig economy has also had a significant impact on society as a whole. Some of these effects include: Economic growth: The gig economy has contributed to economic growth by creating new job opportunities and fostering innovation. Changing workforce demographics: The gig economy has led to an increase in self-employment and the growth of the “gig” workforce, which includes both full-time and part-time workers. Disruption of traditional industries: The gig economy has disrupted traditional industries such as transportation (e.g., Uber and Lyft) and hospitality (e.g., Airbnb), forcing these industries to adapt to new business models. Income inequality: The gig economy has been criticized for contributing to income inequality, as many gig economy workers earn low wages and lack access to traditional benefits. The gig economy has both positive and negative impacts on workers and society. While it offers increased flexibility and entrepreneurial opportunities for some, it also presents challenges such as job insecurity and limited access to benefits. As the gig economy continues to grow, it is essential for governments, businesses, and workers to work together to address these challenges and ensure a fair and sustainable labor market for all.
The Benefits of the Gig Economy for Workers
The Challenges of the Gig Economy for Workers
The Impact of the Gig Economy on Society
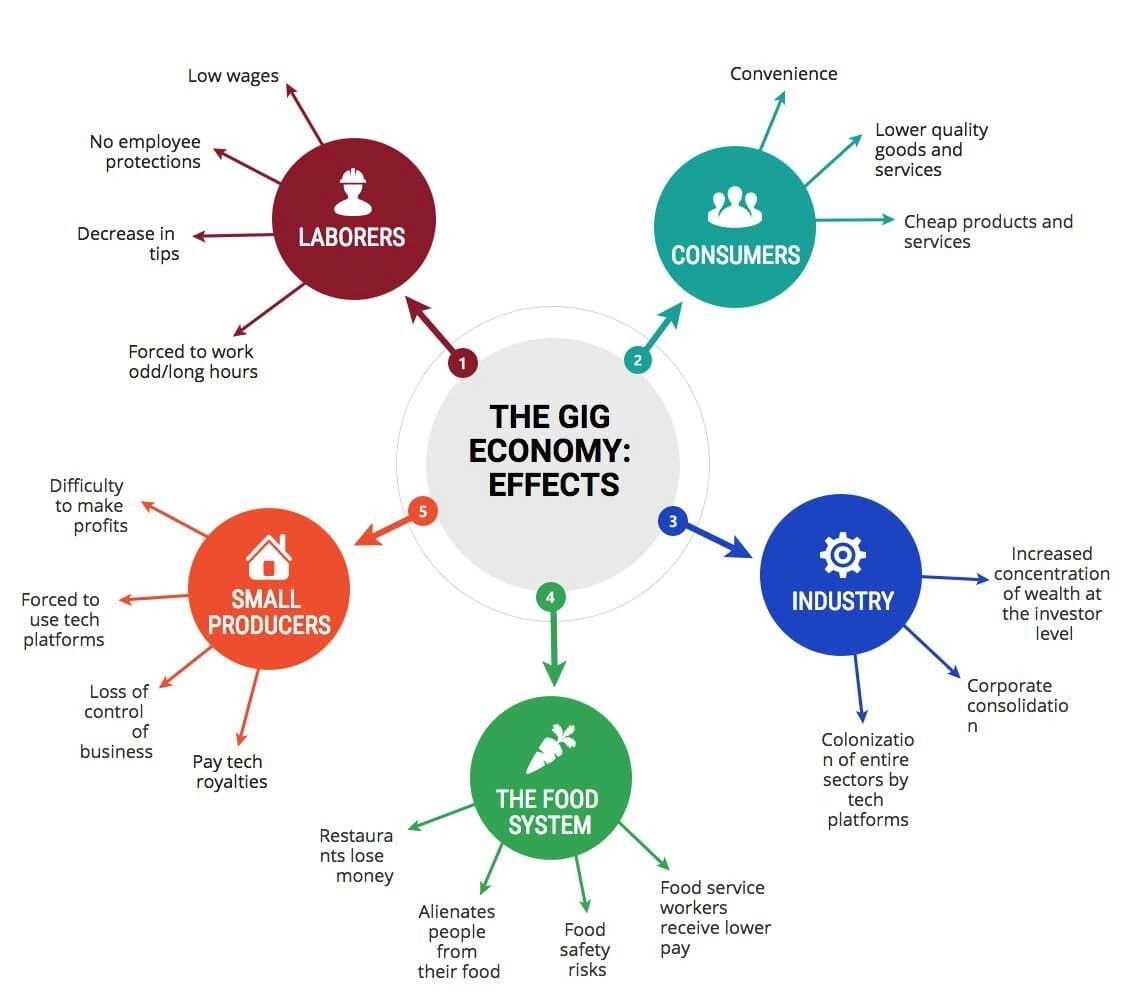
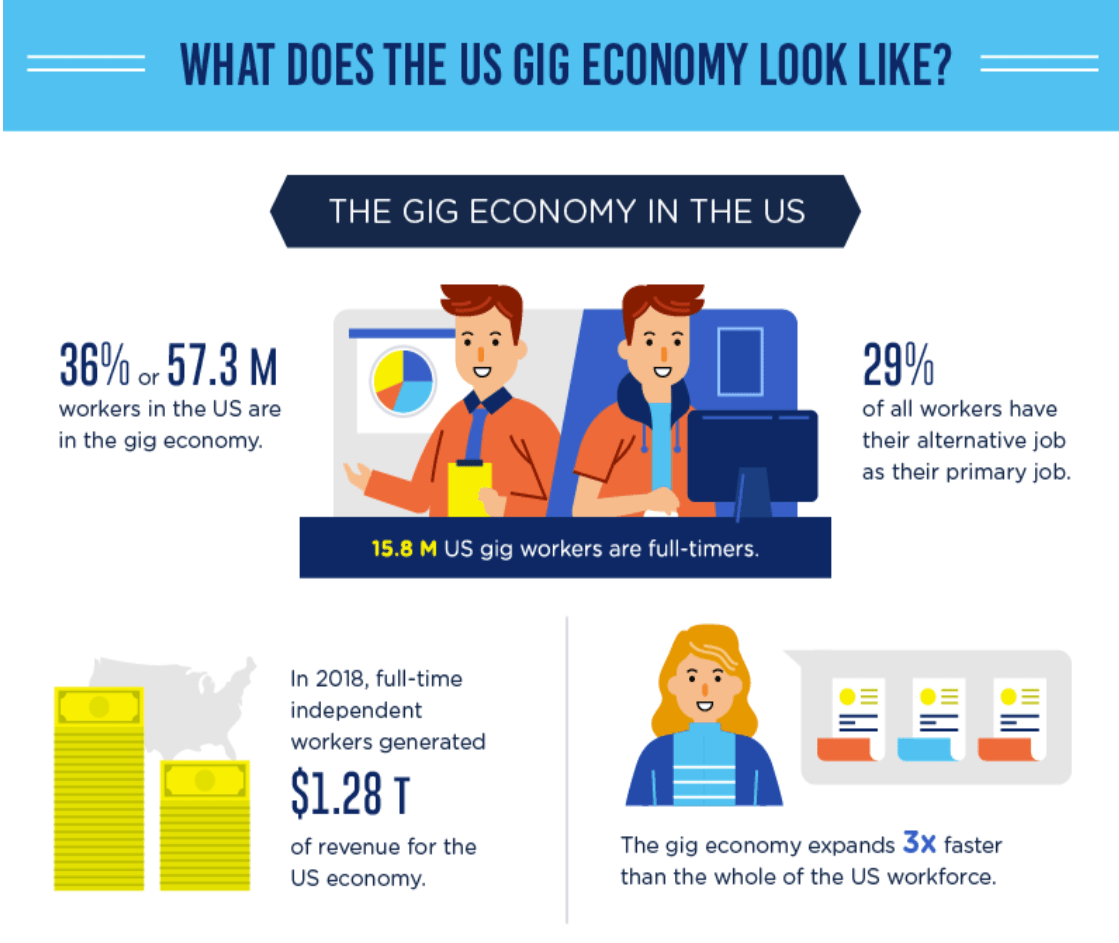
Conclusion
The Influence of AI on Education and Work
In the fast-paced evolution of the digital age, the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force, reshaping various facets of our lives. One of the profound areas experiencing significant change is the intersection of AI with education and work. “The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Education and Work” seeks to unravel the multifaceted impact of AI on these critical domains, exploring how advancements in technology are revolutionizing learning environments, skill requirements, and the very nature of work itself. The advent of AI in education has opened up unprecedented possibilities for personalized learning experiences. This section delves into the ways AI is being integrated into educational systems, from smart tutoring systems that adapt to individual learning styles to AI-powered assessment tools that provide timely feedback. As the digital classroom becomes a reality, the role of teachers evolves, and students engage with education in dynamic, tech-enhanced ways. “The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Education and Work” explores the potential of AI to revolutionize education through personalized learning. AI-driven adaptive systems analyze student performance data to tailor learning experiences, addressing individual strengths and weaknesses. This section investigates how personalized learning can foster a more inclusive and effective educational environment, catering to the diverse needs of students. AI has the potential to bridge educational gaps and make learning accessible to a broader audience. This section delves into the role of AI in promoting inclusivity, breaking down barriers to education faced by individuals with diverse learning needs or those in underserved communities. As AI tools become more sophisticated, they can contribute to democratizing education, offering a pathway to knowledge for learners across the globe. As AI technologies advance, the skill set required in the workforce undergoes a transformation. “The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Education and Work” explores the changing landscape of job requirements, emphasizing the need for a dynamic skill set that includes not only technical proficiency but also critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability. The section examines how educational institutions must adapt to equip students with the skills necessary to thrive in the AI-driven workplace. In the workplace, the integration of AI prompts a shift in the dynamics of collaboration. This section investigates the symbiotic relationship between humans and AI, highlighting how technology can augment human capabilities and enhance productivity. It explores examples of AI applications in various industries, showcasing the potential for collaboration that maximizes the strengths of both human workers and intelligent machines. While AI presents opportunities, it also raises concerns about job displacement. This section delves into the impact of automation on certain job sectors and discusses how the workforce can adapt to these changes. Strategies such as upskilling, reskilling, and fostering a culture of lifelong learning become essential components in navigating the evolving job market shaped by AI technologies. “The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Education and Work” addresses the ethical dimensions inherent in the integration of AI. This section explores issues related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the responsible use of AI in educational and professional settings. As AI becomes more ingrained in society, it is crucial to establish ethical frameworks that ensure fair and transparent practices. In the grand tapestry of technological progress, the influence of Artificial Intelligence on education and work stands as a pivotal chapter. “The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Education and Work” concludes with a reflection on the dynamic interplay between AI and these critical domains. It emphasizes the need for a proactive approach in harnessing the transformative power of AI for educational advancement and workforce evolution. By understanding the potential, challenges, and ethical considerations, society can navigate this technological frontier, ensuring that AI serves as a catalyst for positive change in education and work rather than a disruptive force.
Introduction
AI in Education – A Technological Pedagogue
Personalized Learning and Adaptive Systems

AI as an Educational Equalizer
Skill Evolution in the Age of AI

Collaboration Between Humans and AI
AI and Job Disruption
Ethical Considerations in AI Education and Work

Conclusion
The Role of Social Media in Politics and Activism
Social media has become an integral part of modern society, influencing various aspects of our lives, including politics and activism. The rise of platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and others has transformed the way people engage with political issues and participate in activism. This blog will explore the significant role of social media in shaping political discourse, mobilizing movements, and influencing public opinion. One of the most prominent impacts of social media on politics is its ability to enhance political engagement and awareness among the general public. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook provide a space for politicians to directly communicate with their constituents, share their policy positions, and engage in real-time discussions. This direct interaction allows for a more transparent and accessible form of political communication, enabling citizens to stay informed about current events and political developments. Moreover, social media serves as a powerful tool for raising awareness about political issues that may not receive extensive coverage in traditional media outlets. Users can easily share news articles, opinion pieces, and personal perspectives on various political topics, broadening the scope of information available to the public. This democratization of information empowers individuals to educate themselves about diverse political viewpoints and encourages critical thinking about societal issues. Social media platforms have played a pivotal role in mobilizing grassroots movements and activism on a global scale. The ease of sharing content and organizing events online has facilitated the rapid spread of social and political movements. For instance, the Arab Spring uprisings in 2010-2012 demonstrated how social media platforms were utilized to coordinate protests, disseminate information, and galvanize support for political change across the Middle East. In addition to large-scale movements, social media has empowered individuals to initiate local activism efforts within their communities. Hashtags such as #BlackLivesMatter and #MeToo have gained traction as symbols of solidarity and advocacy for social justice causes. These digital movements have transcended online spaces, sparking offline demonstrations, conversations, and policy reforms. The pervasive nature of social media has also made it a potent force in shaping public opinion on political matters. Through targeted advertising, algorithmic curation of content, and viral sharing mechanisms, social media platforms can amplify specific narratives and viewpoints. This phenomenon has raised concerns about echo chambers and filter bubbles, where users are primarily exposed to information that aligns with their existing beliefs. Furthermore, the spread of misinformation and disinformation on social media has become a pressing issue in the realm of politics. False news stories, manipulated images, and deceptive propaganda can quickly gain traction online, potentially swaying public opinion or sowing confusion during electoral processes. As a result, there is an ongoing debate about the responsibility of social media companies in combating misinformation while preserving freedom of expression. In conclusion, social media has significantly impacted politics and activism by enhancing political engagement and awareness, mobilizing grassroots movements, and influencing public opinion. While it has democratized access to information and facilitated new forms of civic participation, it also presents challenges related to misinformation and polarization. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential to critically examine the role of social media in shaping our collective understanding of politics and activism.
The Role of Social Media in Politics and Activism

Political Engagement and Awareness
Mobilizing Movements and Grassroots Activism

Influencing Public Opinion
Conclusion
The Rise of Remote Work and its Effects on Society
The concept of remote work has been gaining momentum over the past few years, with the COVID-19 pandemic acting as an accelerator for this trend. Remote work refers to the practice of performing job duties and tasks from a location other than the employer’s premises, typically at the employee’s home or other alternative workspace. This mode of work has several advantages for both employers and employees, such as increased flexibility, reduced costs, and a better work-life balance. One of the main reasons for the rise of remote work is the advancement in technology, particularly in communication and collaboration tools. Platforms such as Zoom, Slack, and Microsoft Teams have made it possible for employees to work remotely while still being able to effectively communicate with their colleagues and supervisors. Furthermore, the growth of the gig economy and the increasing number of freelance workers has contributed to the popularity of remote work. Changing workforce dynamics: Remote work has led to a more diverse workforce, as it allows individuals from different geographical locations to contribute to the same project or team. This has resulted in a more inclusive work environment, where individuals with disabilities or those living in remote areas can also participate in the workforce. Environmental impact: Remote work has reduced the need for commuting, which in turn has contributed to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion. Additionally, remote work has encouraged the adoption of environmentally friendly practices, such as teleconferencing and paperless documentation. Work-life balance: Remote work has allowed employees to have greater control over their work schedules, leading to improved work-life balance. This has resulted in reduced stress levels and increased overall well-being for employees. Economic impact: Remote work has led to cost savings for both employers and employees. Employers can save on office space, utilities, and other overhead costs, while employees can save on transportation and other work-related expenses. This has had a positive impact on the economy as a whole. Impact on urbanization: The rise of remote work has led to a shift in urbanization patterns, with people moving away from densely populated urban areas in search of more affordable housing and a better quality of life. This has resulted in the growth of smaller cities and rural areas, which has led to economic development in these regions. Lack of social interaction: Remote work can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, as employees may miss out on the social interactions that occur in a traditional office setting. Difficulty in setting boundaries: Remote work can blur the lines between work and personal life, making it difficult for employees to disconnect from work and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Challenges in managing remote teams: Managers and supervisors may struggle with effectively managing remote teams, as it can be challenging to monitor productivity and ensure that employees are staying on task without direct oversight. Cybersecurity risks: Remote work exposes employees and employers to increased cybersecurity risks, as employees may access sensitive company information from unsecured networks or devices. In conclusion, the rise of remote work has had a significant impact on society, with both positive and negative effects. As technology continues to advance and the workforce becomes more globalized, it is essential for employers, employees, and policymakers to adapt to these changes and find ways to address the challenges that remote work presents.
The Rise of Remote Work

The rise of remote work has had several effects on society. Some of these effects include:
Despite the numerous benefits of remote work, there are also challenges associated with this mode of work. Some of these challenges include:

Nature’s Symphony: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Human and Environmental Health
In the grand tapestry of existence, the harmonious relationship between human health and the environment resembles a complex symphony. “Nature’s Symphony” aims to explore this intricate connection, delving into the ways in which the health of the planet and the well-being of humanity are intertwined. This blog post seeks to understand the delicate balance that exists between the two, emphasizing the importance of nurturing both for a sustainable and thriving future. To comprehend the interconnectedness of human and environmental health, it is essential to recognize the healing power of nature. This section explores the concept of ecotherapy and the positive impact that spending time in natural environments has on mental and physical well-being. From reducing stress to improving mood, nature’s therapeutic effects lay the foundation for understanding the symbiotic relationship between humans and their natural surroundings. “Nature’s Symphony” delves into the critical role of air and water in sustaining life. The quality of the air we breathe and the water we drink directly influences our health. This section explores the consequences of air and water pollution on human health, underscoring the need for environmental conservation efforts to safeguard the essential elements that form the backbone of nature’s symphony. Our sustenance is intricately linked to the health of the environment. This section explores the impact of agriculture and food production on both human health and the planet. From the use of pesticides to the depletion of soil quality, we unravel the complexities of our food system and its consequences on the delicate balance of nature’s symphony. Biodiversity, often considered the conductor of nature’s symphony, plays a crucial role in maintaining the resilience of ecosystems and human health. This section explores the diverse array of benefits that biodiversity provides, from medicinal plants to genetic diversity in agriculture. It emphasizes the need for conservation efforts to protect the rich biodiversity that contributes to the overall harmony of the natural world. The overarching theme of climate change resonates throughout “Nature’s Symphony.” This section explores the impact of a changing climate on human health, from the spread of infectious diseases to the increasing frequency of extreme weather events. Understanding the interconnectedness between human activities and climate patterns is essential for orchestrating a harmonious future for both the planet and its inhabitants. As our world becomes increasingly urbanized, the design of cities and human settlements plays a pivotal role in shaping the interplay between human health and the environment. This section examines the importance of sustainable urban planning, green spaces, and accessibility to nature in promoting the well-being of urban populations. It highlights the need for a harmonious coexistence between urban development and environmental preservation. “Nature’s Symphony” explores the concept of environmental justice, acknowledging that the impacts of environmental degradation disproportionately affect marginalized communities. The interconnectedness between socio-economic factors, environmental health, and human well-being is dissected, emphasizing the importance of equitable and inclusive approaches to environmental conservation and public health. In the final crescendo, “Nature’s Symphony” concludes with a reflection on the interwoven threads of human and environmental health. It emphasizes the urgency of adopting holistic approaches that consider the intricate connections between the two. By fostering a deeper understanding of this symbiotic relationship, we can compose a future where the health of the planet and the well-being of humanity resonate in harmony, creating a symphony that echoes through generations to come.
Introduction
The Healing Power of Nature
Air we Breathe, Water we Drink

The Food Connection
Biodiversity and Human Resilience

Climate Harmony
Urban Planning and Public Health
The Role of Environmental Justice
Conclusion
Sustainable Business Practices: A Guide to Eco-Friendly Operations
In an era where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global discourse, businesses are increasingly recognizing the imperative to adopt sustainable practices. This post serves as a comprehensive guide to eco-friendly operations, exploring the principles, benefits, and practical strategies that businesses can implement to align with sustainability goals. Sustainable business practices go beyond merely complying with environmental regulations. They involve a holistic approach to conducting operations that minimizes negative impacts on the environment, society, and the economy. The aim is to create a balance where present actions do not compromise the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Sustainability is often described in terms of three interconnected pillars: environmental, social, and economic. These pillars form the foundation for businesses seeking to operate in a sustainable manner. Embracing sustainable business practices is not just an ethical choice; it also makes good business sense. There are several compelling reasons for businesses to prioritize sustainability: Sustainable business practices are not just a trend; they are a fundamental shift in the way businesses operate in the 21st century. Embracing sustainability is not only a moral obligation but a strategic imperative for long-term success. By adopting eco-friendly operations, businesses can contribute to a healthier planet, build resilience in the face of environmental challenges, and position themselves as leaders in a market that increasingly values sustainability. This guide provides a roadmap for businesses to embark on their sustainability journey, promoting a harmonious coexistence of economic prosperity, social well-being, and environmental stewardship.Understanding Sustainable Business Practices
The Three Pillars of Sustainability
The Business Case for Sustainability

Practical Strategies for Eco-Friendly Operations
1. Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy:
2. Waste Reduction and Recycling:
3. Supply Chain Sustainability:
4. Green Building Practices:
5. Employee Engagement and Well-Being:
6. Circular Economy Practices:
7. Water Conservation:
8. Community Outreach and Social Responsibility:
9. Transparency and Reporting:
10. Innovation and Continuous Improvement:
Conclusion










