Voice Assistants and Privacy Concerns: Navigating the Trade-off
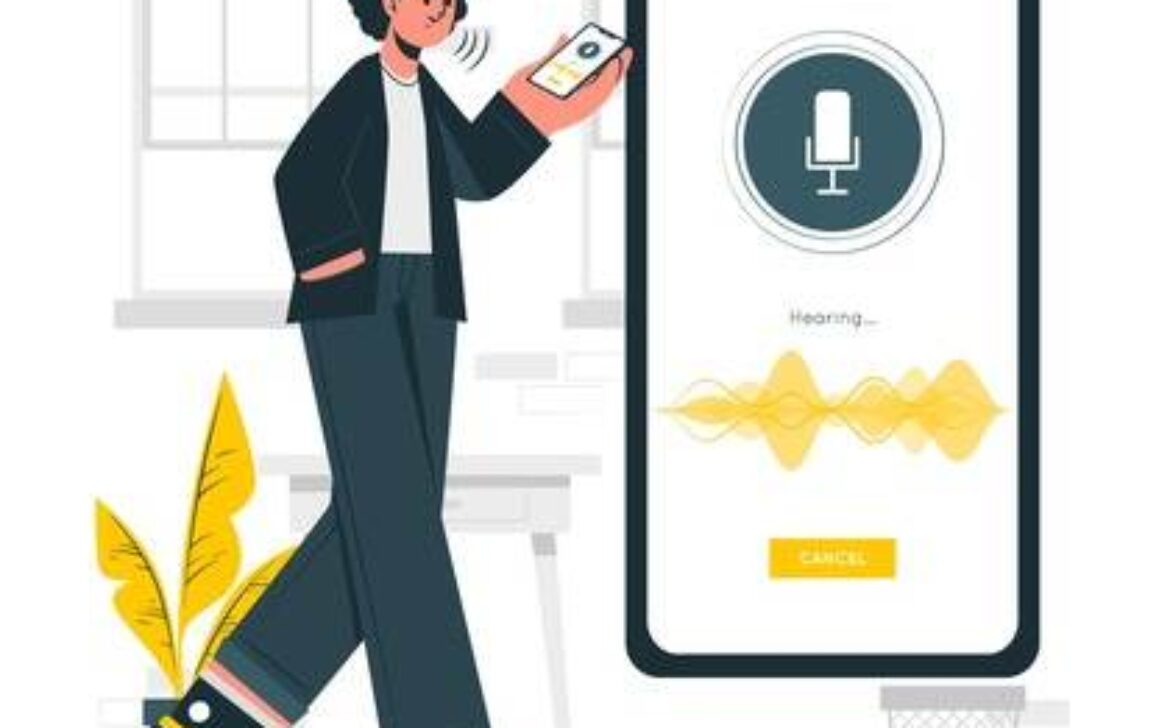
In a world of rapidly advancing technology, voice assistants have become an integral part of our daily lives. These intelligent virtual helpers, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Microsoft’s Cortana, offer convenience and efficiency like never before. They can perform tasks, answer questions, play music, control smart devices, and even engage in casual conversations.
The Rise of Voice Assistants
Voice assistants have witnessed an explosive growth in recent years, transforming the way we interact with technology. With just a simple voice command, users can access a plethora of information and services, making tasks hands-free and effortless.
How Voice Assistants Work
These virtual assistants utilize natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand and respond to user commands. They continuously learn from user interactions to enhance their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Convenience at Our Fingertips
One of the primary benefits of voice assistants is the convenience they offer. From setting reminders and sending texts to ordering groceries, voice commands streamline daily tasks, saving both time and effort.
The Privacy Predicament
While voice assistants offer undeniable benefits, the collection of audio data raises significant privacy red flags. Conversations within earshot can be inadvertently recorded and stored by the assistant’s parent companies, leading to potential breaches of sensitive information.
Data Security and Storage
Voice recordings are stored on servers for analysis and improvement of the assistants’ capabilities. Companies claim they anonymize the data, but concerns persist over the potential identification of individuals through voice patterns and context.
Vulnerabilities to Hacks and Breaches
Hackers pose a risk to the data stored by voice assistants. Unauthorized access to voice recordings could expose personal conversations, financial details, and other sensitive information.
User Consent and Control
Many users remain unaware of the extent of data collection by voice assistants. Providing clearer information about data usage and enhancing user controls are crucial steps toward addressing privacy concerns.
Balancing Personalization and Privacy
Voice assistants thrive on personalization, learning user preferences for tailored experiences. Striking a balance between customization and maintaining user privacy is a delicate challenge.
Regulatory Measures
Governments and regulatory bodies are stepping in to establish guidelines for data collection and usage by voice assistants. Compliance with these regulations is essential to protect user privacy.
Securing Voice Assistant Devices
Manufacturers are investing in improved security measures to safeguard voice assistant devices. Encryption and better authentication methods aim to prevent unauthorized access.
User Education
Educating users about the risks and best practices surrounding voice assistants is crucial. This empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their usage and data sharing.
Future Trends and Innovations
The evolution of voice assistants continues, with advancements in privacy-focused technologies, including on-device processing and improved data anonymization.
Exploring Alternatives
Some individuals are exploring alternative voice assistant options that prioritize privacy, limiting data sharing and storing information locally.
The Ethical Dimension
The ethical implications of voice assistants involve balancing technological progress with fundamental human rights, such as privacy and consent.
Navigating the Trade-off
As we move forward in the age of voice assistants, striking a balance between the undeniable convenience they offer and the privacy concerns they raise becomes paramount.
Conclusion
Voice assistants have undoubtedly revolutionized our interaction with technology, yet the concerns about privacy and data security cannot be overlooked. Navigating this trade-off requires a collaborative effort from technology companies, regulators, and users themselves. By prioritizing transparency, consent, and security, we can harness the power of voice assistants while safeguarding our personal information.